Identify the true and false statements about antipsychotics. – In the realm of psychiatry, antipsychotics play a pivotal role in managing mental health conditions. This discourse delves into the complexities of antipsychotic medications, examining their purpose, types, effectiveness, and potential side effects. By exploring both true and false statements about antipsychotics, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of these essential medications.
Antipsychotics, as the name suggests, are primarily utilized to treat psychotic disorders, particularly schizophrenia. Their efficacy in managing symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking has been well-established. However, their use extends beyond schizophrenia, as they also play a role in mitigating symptoms of bipolar disorder and other conditions.
Antipsychotic Medications

Antipsychotic medications are used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and psychosis. They work by blocking the effects of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is involved in the regulation of mood, thought, and behavior.
Types of Antipsychotic Medications, Identify the true and false statements about antipsychotics.
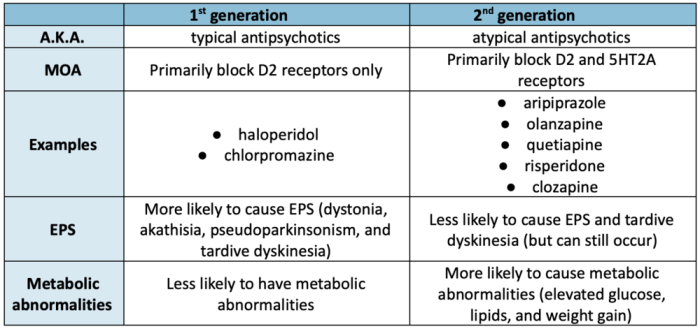
There are two main types of antipsychotic medications: typical and atypical. Typical antipsychotics, such as haloperidol and chlorpromazine, are older medications that are effective in treating the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations and delusions. However, they can also cause significant side effects, such as movement disorders and tardive dyskinesia.
Atypical antipsychotics, such as risperidone and olanzapine, are newer medications that are more effective in treating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia, such as social withdrawal and lack of motivation. They also have a lower risk of causing side effects than typical antipsychotics.
Common Side Effects of Antipsychotic Medications
The most common side effects of antipsychotic medications include:
- Drowsiness
- Weight gain
- Movement disorders
- Tardive dyskinesia
- Hyperprolactinemia
True and False Statements about Antipsychotics
True:Antipsychotics are used to treat schizophrenia.
False:Antipsychotics are not effective in treating bipolar disorder.
True:Antipsychotics can cause weight gain.
False:Antipsychotics are addictive.
Effectiveness of Antipsychotics: Identify The True And False Statements About Antipsychotics.
Antipsychotic medications are effective in treating the symptoms of schizophrenia. They can reduce hallucinations, delusions, and other positive symptoms, and they can improve social functioning and cognitive abilities. Antipsychotics are also effective in treating bipolar disorder, and they can help to prevent episodes of mania and depression.
However, antipsychotic medications are not a cure for schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. They can only manage the symptoms of these conditions, and they need to be taken on a regular basis to be effective.
Side Effects of Antipsychotics
Antipsychotic medications can cause a variety of side effects, including:
- Drowsiness
- Weight gain
- Movement disorders
- Tardive dyskinesia
- Hyperprolactinemia
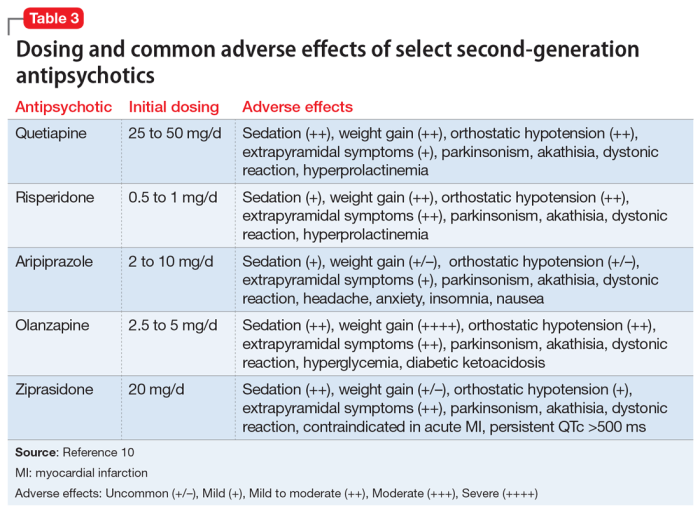
The most common side effect of antipsychotic medications is drowsiness. This side effect is usually mild and goes away after a few weeks of treatment. However, some people may experience more severe drowsiness, which can interfere with their daily activities.
Weight gain is another common side effect of antipsychotic medications. This side effect is usually gradual and can occur over several months. Weight gain can be a problem for some people, as it can lead to obesity and other health problems.
Movement disorders are a group of side effects that can occur with antipsychotic medications. These side effects include tremors, muscle spasms, and rigidity. Movement disorders can be mild or severe, and they can interfere with a person’s ability to move and function.
Tardive dyskinesia is a serious side effect of antipsychotic medications that can develop after long-term use. Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by involuntary movements of the face, mouth, and tongue. These movements can be disfiguring and can interfere with a person’s ability to eat, speak, and swallow.
Hyperprolactinemia is a side effect of antipsychotic medications that can lead to increased levels of prolactin in the blood. Prolactin is a hormone that is involved in the production of breast milk. Hyperprolactinemia can cause a variety of side effects, including breast enlargement, galactorrhea (the production of breast milk in women who are not breastfeeding), and menstrual irregularities.
Alternatives to Antipsychotics
There are a number of alternative treatments for schizophrenia, including psychotherapy, social skills training, and cognitive behavioral therapy. These treatments can help to improve symptoms and functioning, and they can be used in combination with antipsychotic medications.
Psychotherapy is a type of talk therapy that can help people with schizophrenia to understand their condition and develop coping mechanisms. Social skills training can help people with schizophrenia to improve their social skills and relationships. Cognitive behavioral therapy can help people with schizophrenia to change their negative thoughts and behaviors.
User Queries
Are antipsychotics addictive?
No, antipsychotics are not typically addictive in the traditional sense. They do not produce the same euphoric effects as substances of abuse, and their discontinuation does not usually lead to withdrawal symptoms.
Can antipsychotics cause weight gain?
Yes, weight gain is a common side effect of certain antipsychotics. The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve alterations in metabolism and appetite regulation.
Are antipsychotics effective for all mental health conditions?
No, antipsychotics are primarily effective for treating psychotic disorders. They may have limited efficacy for other mental health conditions, such as anxiety or depression, and may even worsen symptoms in some cases.