Symbiotic relationships worksheet good buddies – Delving into the fascinating world of symbiotic relationships, the Symbiotic Relationships Worksheet: Good Buddies introduces us to the intricate and mutually beneficial partnerships that shape the natural world. From the harmonious coexistence of mutualism to the complexities of commensalism and parasitism, this worksheet explores the diverse spectrum of symbiotic interactions that drive the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Mutualistic relationships, where both organisms derive benefits from their association, are a testament to the power of cooperation. Commensalism, on the other hand, offers unilateral advantages, while parasitism involves one organism exploiting another for its own survival. Understanding these symbiotic dynamics is crucial for unraveling the intricate web of life that sustains our planet.
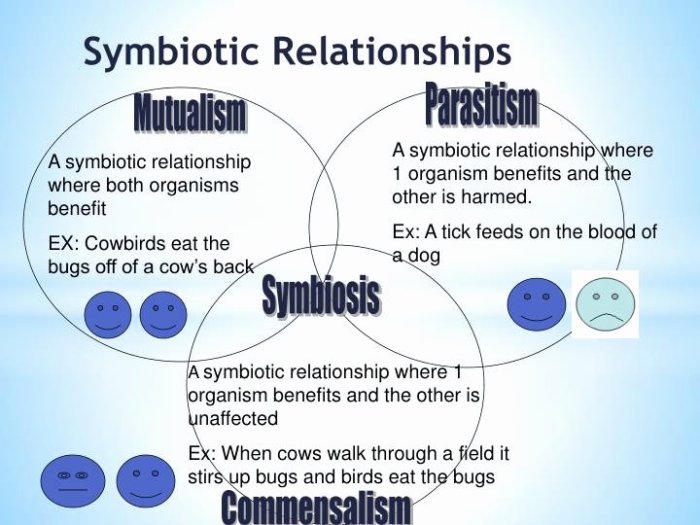
Symbiotic Relationships: An Overview

Symbiotic relationships are close and long-term interactions between different species that have evolved to benefit one or both partners.
These relationships can be classified into three main types:
- Mutualism: both species benefit from the relationship.
- Commensalism: one species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
- Parasitism: one species benefits at the expense of the other.
Benefits and Challenges of Symbiotic Relationships
The benefits of symbiotic relationships can include increased access to resources, protection from predators, and enhanced reproductive success.
However, symbiotic relationships can also pose challenges, such as competition for resources, transmission of diseases, and the potential for exploitation.
Good Buddies: Exploring Mutualistic Symbiosis: Symbiotic Relationships Worksheet Good Buddies

Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit from the interaction.
Examples of Mutualistic Relationships
- Pollination between plants and insects
- Nitrogen fixation between plants and bacteria
- Cleaning symbiosis between fish and cleaner shrimp
Mutualistic relationships often involve the exchange of resources or services that neither species could obtain independently.
Evolutionary Pressures Driving Mutualism
Mutualistic relationships are driven by evolutionary pressures that favor cooperation and interdependence.
Species that can form mutually beneficial relationships may have a selective advantage over those that cannot.
The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly: Commensalism and Parasitism
Commensalism and parasitism are symbiotic relationships that can have varying degrees of benefit or harm for the organisms involved.
Commensalism
- One species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
- Examples: Barnacles attached to whales, epiphytes growing on trees
Parasitism
- One species benefits at the expense of the other.
- Examples: Tapeworms in the intestines of animals, fleas on dogs
Parasitism can range from benign to deadly, depending on the severity of the infection and the immune response of the host.
Symbiotic Relationships in the Real World
Symbiotic relationships are ubiquitous in nature and play a vital role in the functioning of ecosystems.
- Pollination by insects is essential for the reproduction of many plant species.
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria enable plants to access nitrogen from the atmosphere.
- Coral reefs are formed through a mutualistic relationship between corals and algae.
Symbiotic relationships also have implications for human society, such as the use of probiotics in medicine and the role of bees in agriculture.
Visualizing Symbiosis: HTML Table Representation
The following HTML table provides a summary of different symbiotic relationships:
| Type of Relationship | Organisms Involved | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mutualism | Pollinators and plants | Increased pollination success, access to nectar | Competition for resources |
| Commensalism | Barnacles and whales | Attachment surface for barnacles | None for whales |
| Parasitism | Tapeworms and animals | Nutrients for tapeworms | Damage to host’s tissues |
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Symbiotic Concepts
Symbiotic relationships are complex and can extend beyond the basic categories of mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
Coevolution in Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiotic relationships can drive coevolution, where both species evolve in response to the presence of the other.
This can lead to the development of specialized adaptations that enhance the benefits of the relationship.
Role in Speciation and Biodiversity
Symbiotic relationships can contribute to speciation and increase biodiversity.
For example, mutualistic relationships between plants and pollinators can lead to the formation of new plant species.
Applications in Biotechnology and Medicine, Symbiotic relationships worksheet good buddies
Symbiotic relationships have potential applications in biotechnology and medicine.
For instance, scientists are exploring the use of probiotics to treat various health conditions.
Clarifying Questions
What are the main types of symbiotic relationships?
Mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism are the three main types of symbiotic relationships.
What are the benefits of mutualistic relationships?
Mutualistic relationships provide benefits to both organisms involved, such as increased access to resources, protection from predators, or enhanced reproductive success.
How do parasitic relationships differ from commensalistic relationships?
In parasitic relationships, one organism benefits at the expense of the other, while in commensalistic relationships, one organism benefits without harming or benefiting the other.