Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of chemical bonding with our comprehensive Types of Bonds Chemistry Worksheet. This guide delves into the fundamental concepts of covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds, unraveling their characteristics, formation mechanisms, and comparative properties.
Prepare to deepen your understanding of these essential chemical interactions.
Covalent bonds, characterized by the sharing of electron pairs between atoms, form the backbone of organic molecules and determine their reactivity. Ionic bonds, on the other hand, result from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, shaping the properties of salts and ionic compounds.
Metallic bonds, unique to metals, arise from the delocalization of valence electrons, giving rise to exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity.
Types of Chemical Bonds: Types Of Bonds Chemistry Worksheet
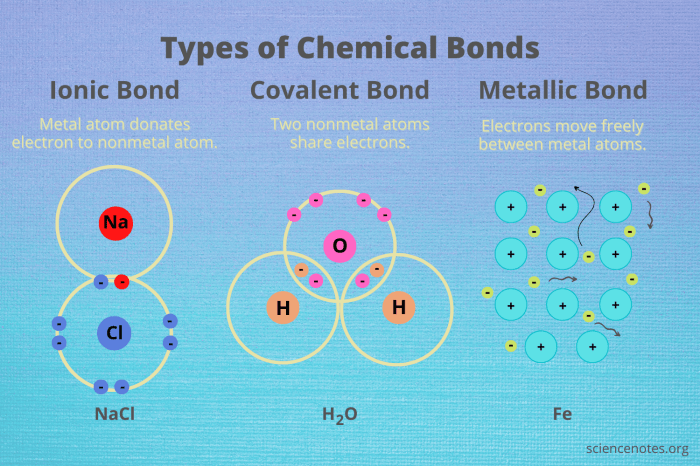
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are three main types of chemical bonds: covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons. The electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, which holds the atoms together. Covalent bonds are the strongest type of chemical bond.
Examples of covalent bonds include the bonds between the atoms in hydrogen gas (H 2), water (H 2O), and methane (CH 4).
| Property | Covalent Bonds |
|---|---|
| Strength | Strong |
| Polarity | Nonpolar or polar |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| Electrical Conductivity | Poor conductors of electricity |
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom gives up one or more electrons to another atom. The atoms are then attracted to each other by the opposite charges of their ions.
Examples of ionic bonds include the bonds between the atoms in sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium fluoride (KF), and calcium oxide (CaO).
- Ionic bonds are typically formed between a metal and a nonmetal.
- Ionic bonds are strong and brittle.
- Ionic compounds are soluble in water.
- Ionic compounds are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or melted.
Metallic Bonds, Types of bonds chemistry worksheet
Metallic bonds are formed between metal atoms. The metal atoms share their valence electrons in a sea of electrons.
Metallic bonds are strong and ductile.
Metallic compounds are good conductors of electricity and heat.
An illustration of a metallic bond:
[Insert illustration of a metallic bond here]
Essential Questionnaire
What is the key difference between covalent and ionic bonds?
Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs, while ionic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
How do metallic bonds contribute to the properties of metals?
Metallic bonds, formed by the delocalization of valence electrons, impart exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity to metals.